A * B * Ċ * C * D * E * F *
Ġ * G * GĦ * H * Ħ * I * J * K *
L * M * N * O * P * Q * R * S *
T * U * V * W * X * Ż * Z *
Since time immemorial, there have been many great story-tellers, the world over. In Greek times there was Aesop with his fables, who entertained while providing moral lessons, and Homer with his epic tales that extolled the prowess of the Greek gods. In the Indian, Persian and Arab world too, one finds a collection of fantastic tales in ‘One Thousand and One Nights’. In Europe, famous writers, such as the German Grimm Brothers, and the Danish Hans Christian Anderson, created characters that still enthral millions. Some of these tales, do have parallels in distant countries, as they were spread by word of mouth to be adopted by other cultures. Maltese tales were not excluded from such influences. On the contrary some local folk tales seem to connect with similar ones in North Africa, in nearby Sicily as well as certain countries in Europe and the Middle East.
 Story-telling is a pastime that may be performed to the enjoyment of children and adults alike. There still exists in the English vernacular an idiomatic expression that goes, ‘to spin a yarn’. This idiom could very well fit in a practical way, the Maltese way of life, of some 200 years ago, during the time when the cotton industry thrived. Hundreds of workers, mostly made up of the farmers’ own family gathered in rooms or courtyards of their residence, to gin and spin cotton into yarn. This time-consuming process was often done by the womenfolk accompanied by their young children. One may imagine that in order to cheer themselves up during the laborious and tedious hours, the matriarchal figure of the family, most often the oldest women of the group, recounted anecdotes and tales to entertain those working or idling nearby. This may have been one way how oral tradition filtered down from one generation to the next.
Story-telling is a pastime that may be performed to the enjoyment of children and adults alike. There still exists in the English vernacular an idiomatic expression that goes, ‘to spin a yarn’. This idiom could very well fit in a practical way, the Maltese way of life, of some 200 years ago, during the time when the cotton industry thrived. Hundreds of workers, mostly made up of the farmers’ own family gathered in rooms or courtyards of their residence, to gin and spin cotton into yarn. This time-consuming process was often done by the womenfolk accompanied by their young children. One may imagine that in order to cheer themselves up during the laborious and tedious hours, the matriarchal figure of the family, most often the oldest women of the group, recounted anecdotes and tales to entertain those working or idling nearby. This may have been one way how oral tradition filtered down from one generation to the next.
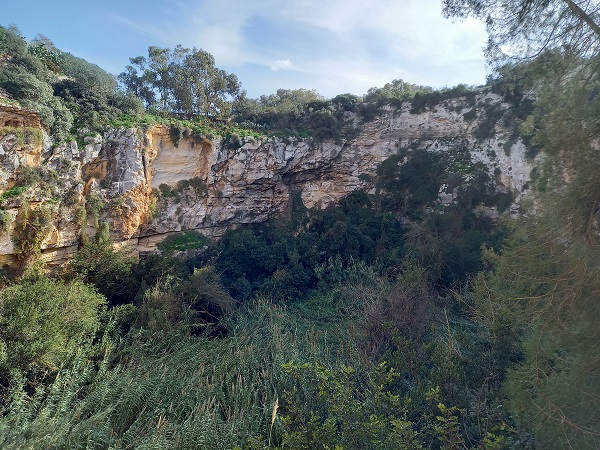

In Malta we come across a variety of folktales. Some of these accounts served to explain the peculiar phenomena of nature, such as astronomical observations, changing weather conditions, geological occurrences and even the origin of place-names. One may cite the case of the legendary sinkhole that exists near the village of Qrendi, known as Il-Maqluba, (M. the overturned). Legend has it that at that location there was once a village whose inhabitants lacked moral rectitude. To punish them, God destroyed the village and made it disappear from the face of the earth, thus leaving behind a deep pit in which today lush vegetation grows.
The Pioneers of Maltese folklore
At the turn of the twentieth century, various folkorists, most of them foreigners, collected oral folk-tales by interviewing people all over the Maltese islands. One of them was the Italian Luigi Bonelli. Two others were the Germans, Bertha Ilg and Hans Stumme. Then there was the Maltese Jesuit priest, Manwel Magri, (1851 – 1907). Between them they recorded some 100 local tales that may have included a few legends and variants of them. Father Magri recorded 62 folk tales that also included variants. It is interesting to note that of these, about eight recount tales related to menacing giants and fantastic monsters. Sixteen other tales involve imaginary kings, known by the Maltese as is-Sultan, a despotic ruler whose authority they feared as he was bound to threaten to his subjects by irrational edicts. The Sultan held power over life and death over one and all.
Giants and Megaliths A couple of tales may be classified as legends. For instance some tend to provide a reason why the mysterious Maltese prehistoric megalithic temples were built by giants. One such tale In Gozo recounts how a giantess, whom legend has it was called Sansuna, transported a menhir from the small village of Sannat a large boulder on her shoulder to set it up at the village of Qala, where it is still stands today. This she did with ease, sustaining herself by consuming broad beans (M. ful). The megalithic temples of Ġgantija at Xagħra, as the name implies, were supposedly built by giants. Even Gian Franġisk Abela, Malta’s most ancient historian, wrote in his Della Descrittione di Malta (1647), that he believed that the Maltese temples were built by a race of giants that inhabited the islands in Pre-Deluvian times. This belief was corroborated by the occasional finds of large-sized skeletal bones in quarries and rock fissures. These remains, in reality, belonged to extinct animal species such as elephants and hippopotami, dating to the glacial and inter-glacial periods Malta.
A couple of tales may be classified as legends. For instance some tend to provide a reason why the mysterious Maltese prehistoric megalithic temples were built by giants. One such tale In Gozo recounts how a giantess, whom legend has it was called Sansuna, transported a menhir from the small village of Sannat a large boulder on her shoulder to set it up at the village of Qala, where it is still stands today. This she did with ease, sustaining herself by consuming broad beans (M. ful). The megalithic temples of Ġgantija at Xagħra, as the name implies, were supposedly built by giants. Even Gian Franġisk Abela, Malta’s most ancient historian, wrote in his Della Descrittione di Malta (1647), that he believed that the Maltese temples were built by a race of giants that inhabited the islands in Pre-Deluvian times. This belief was corroborated by the occasional finds of large-sized skeletal bones in quarries and rock fissures. These remains, in reality, belonged to extinct animal species such as elephants and hippopotami, dating to the glacial and inter-glacial periods Malta.
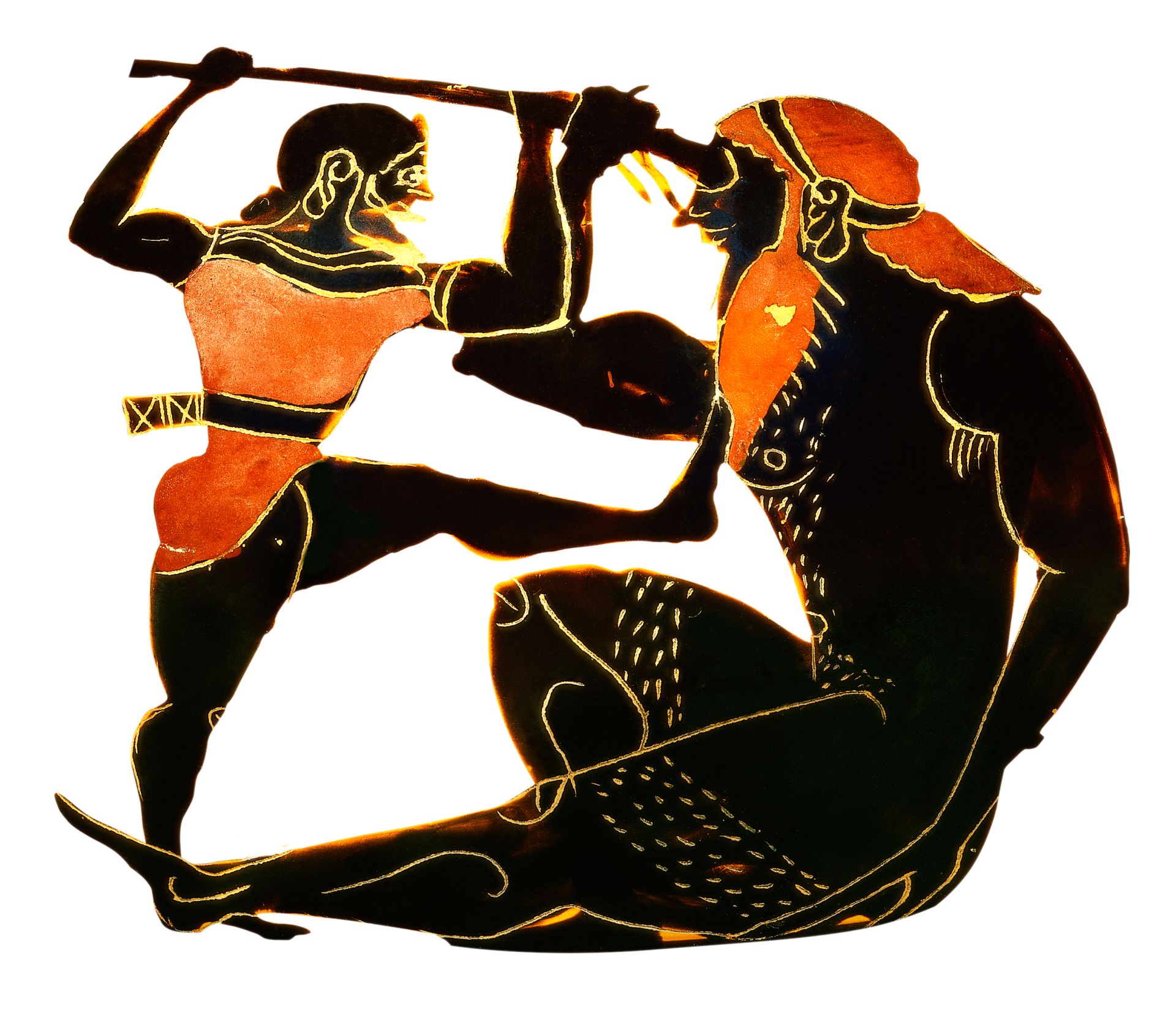 Such fossils are not unique to Malta. Similar finds occur elsewhere in the Mediterranean. It was because of such oversized bones that the Greeks believed in a giant race, known as the Cyclops. These one-eyed creatures, made famous by Homer in his Odyssey, were creatures of fantasy as people believed that the central large cavity in the fossilised elephant skull to which the elephant’s proboscid is attached, instead served to fit and retain the one eye of this creature.
Such fossils are not unique to Malta. Similar finds occur elsewhere in the Mediterranean. It was because of such oversized bones that the Greeks believed in a giant race, known as the Cyclops. These one-eyed creatures, made famous by Homer in his Odyssey, were creatures of fantasy as people believed that the central large cavity in the fossilised elephant skull to which the elephant’s proboscid is attached, instead served to fit and retain the one eye of this creature.
Of the eight giants’ tales, there are included the following, titled: ‘The woman who carried the huge stones for building’. ‘A young boy kills nine giants’; ‘The giants’ bastions’; ‘The giant and the bird hunter’, and ‘A girl kills the giantess’. I shall summarise here the last two to elaborate the gist of these last two tales.
The giant and the bird hunter Once upon a time there was a hunter who ventured into the woods and who came by chance upon a giant. The giant confronts the hunter and challenges him to a wrestling match before devouring him. The hunter keeps his cool and retorts that not even dogs behave like that before they attack one another – they would first sniff at each other before engaging in a fight’. He thus challenged the giant to a contest of skills to prove to him that whatever the latter did he could outdo him. The giant picks up a pebble (Mt. ċagħka), places it in the palm of his hand and crushes it to dust. Not to be outdone, the hunter kneels down to the ground while seccretly takes out a ġbejna (a typical Maltese cheeselet) from his hunting pouch, hides it in the palm of his hand, while he seemingly picks up a pebble from the ground. The white cheeselet was indistinguishable from the pebble and so the hunter shows it to the giant and then proceeds to crush it by pressing his palm into fist. The juices inside the ġbejna spurt out from between his fingers. The giant is amazed that this mere mortal is able to crush the pebble so hard as to liquify its matter. The challenge is followed by others, that the hunter always wins by his wit and his clever tricks. Eventually the giant lets the man go.
Once upon a time there was a hunter who ventured into the woods and who came by chance upon a giant. The giant confronts the hunter and challenges him to a wrestling match before devouring him. The hunter keeps his cool and retorts that not even dogs behave like that before they attack one another – they would first sniff at each other before engaging in a fight’. He thus challenged the giant to a contest of skills to prove to him that whatever the latter did he could outdo him. The giant picks up a pebble (Mt. ċagħka), places it in the palm of his hand and crushes it to dust. Not to be outdone, the hunter kneels down to the ground while seccretly takes out a ġbejna (a typical Maltese cheeselet) from his hunting pouch, hides it in the palm of his hand, while he seemingly picks up a pebble from the ground. The white cheeselet was indistinguishable from the pebble and so the hunter shows it to the giant and then proceeds to crush it by pressing his palm into fist. The juices inside the ġbejna spurt out from between his fingers. The giant is amazed that this mere mortal is able to crush the pebble so hard as to liquify its matter. The challenge is followed by others, that the hunter always wins by his wit and his clever tricks. Eventually the giant lets the man go.
Another fable recounts the story of a small girl who was lame and who was held captive by two giants, a husband and wife, in their home with the intention that some day they would bake her in the oven and devour her as their lunch. The day finally arrives, and while the husband is away, the giantess decides to give her husband a treat by cooking the girl for his lunch. The giantess lets the girl out of her cage and tells her to come over in the kitchen to help her with her cooking. The giantess asks the girl to hop on to the oven’s ledge so that she can teach her how to bake bread. The girl sees what is coming for her. So when they approach the oven the girl suggests to the giantess to sit on the ledge of the oven herself so that she (the girl) would teach her something else. The dim-witted giantess does as she is told. Once the giantess positions herself on the ledge of the oven, the girl promptly shoves her through the oven window and slams the door behind her. She stokes the fire and makes a good giant roast out of her captor. The cooking was ready by the time the giantess’s companion returns home and the girl serves him the nice giant rump for him to devour. However, the story does not finish there.
Following lunch, the giant instructs the girl to fetch him a glass of water from the well. The girl laments that there is not enough water in the well and she suggests that the best way to retrieve the little water there is, she would hoist him down the shaft by a rope so that he would dredge the last bit of water from the bottom into the bucket. The dim-witted giant obliges, and is hoisted down to the bottom of the well. He fills up the bucket with water. Then he cries out, ‘I am ready … you may haul me up young girl!’ The smart young lady says to the giant: ‘You must first say appa! (Appa is a meaningless Maltese word used to poke fun at a given situation). The giant obliges and says ‘appa!‘ to which the girl mockingly replies with a rhyming expression: ‘il-ħabel skappa’ (the rope just slipped), and the girl lets the rope fall down the shaft, thus leaving the giant in the bottom of the well to die.
In all the tales, whenever giants intimidate humans, we observe that these creatures, threatening as they may be, are no match for the witty minds of their puny human adversaries. Both stories cited and others are entertaining to the listener as the hero of the tale emerges unscathed in the end. The story plot works on the premise that brains are more efficacious than brawn in order for one to win any daunting challenge. In the second of these tales, the empathy of the reader is even stronger as the hero of the story is a lame young lady.
Tyrannical Sultans and defying heroes
In Maltese folklore another cluster of tales abound that deal with the whimsical wishes of the authoritative and tyrranical monarch, the Sultan*. The nemesis of the king would be depicted as a simple young man often hailing from a poor family, yet audacious, smart and ready to try his luck by wandering away from home in search of adventure. The hero of the story would be summoned by the king to show his mettle in undergoing some perilous tasks, such as slaying fabulous serpents, monstrous birds, or even towering giants. In return the king promises riches and sometimes the hands of his daughter in marriage. But he would often be threatening the young lad with execution, should the bold lad fail in his tasks. Riddles were sometimes posed to the young contestant to solve in order to progress in his mission. Occasionally, the hero of the story would be the youngest of three brothers or more. Whilst the older brothers fail in their tasks to satisfy the king’s wishes, the younger one succeeds, using his wit, albeit, often aided with the wisdom provided to him by older wise men or women that he comes across during his journey. Knowing that the hero of the tale is young, adventerous and artful while ready to risk his life, makes the listener of the tale empathise totally with him.
tyrranical monarch, the Sultan*. The nemesis of the king would be depicted as a simple young man often hailing from a poor family, yet audacious, smart and ready to try his luck by wandering away from home in search of adventure. The hero of the story would be summoned by the king to show his mettle in undergoing some perilous tasks, such as slaying fabulous serpents, monstrous birds, or even towering giants. In return the king promises riches and sometimes the hands of his daughter in marriage. But he would often be threatening the young lad with execution, should the bold lad fail in his tasks. Riddles were sometimes posed to the young contestant to solve in order to progress in his mission. Occasionally, the hero of the story would be the youngest of three brothers or more. Whilst the older brothers fail in their tasks to satisfy the king’s wishes, the younger one succeeds, using his wit, albeit, often aided with the wisdom provided to him by older wise men or women that he comes across during his journey. Knowing that the hero of the tale is young, adventerous and artful while ready to risk his life, makes the listener of the tale empathise totally with him.
The titles of the Sultan tales include: ‘The baker’s son sets three riddles to the Sultan’s daughter’; ‘The Sultan’s daughter answers no to three questions’; ‘The eighth son saves the Sultan’s daughter from the dragon’; ‘The son of the wise woman makes the bird sing’. Then there is ‘The tale of the old man buried in the cave’, which I shall recount briefly to elucidate on the arguments given above.
The tale of the old man buried in a cave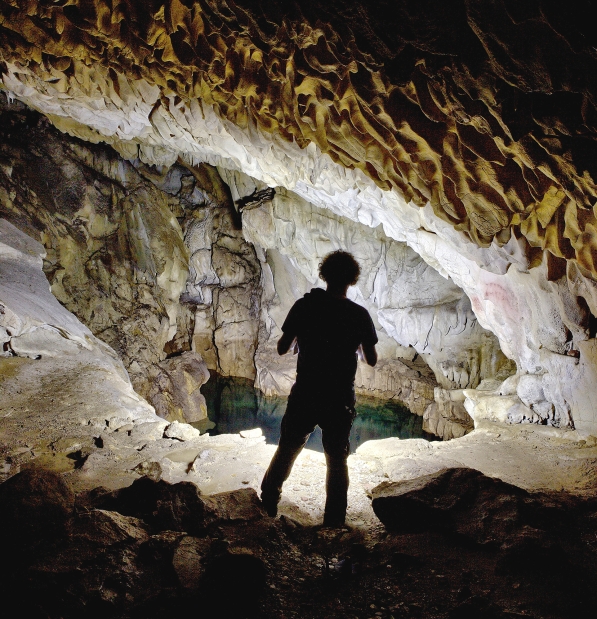 In this tale, a young lad takes his old and decrepit father to the ‘cave of death’ where as custom dictates, the old man is imprisoned in order for him to die soon in his own ‘tomb’. Such a sepulchral cave is known in Maltese folklore as a demus. In any case, while blocking the cave by an outside wall to imprison his father, the boy takes pity on him and so he leaves a small opening for his father to breathe in some fresh air. Moreover, he decides to return regularly to nourish him with goat’s milk.
In this tale, a young lad takes his old and decrepit father to the ‘cave of death’ where as custom dictates, the old man is imprisoned in order for him to die soon in his own ‘tomb’. Such a sepulchral cave is known in Maltese folklore as a demus. In any case, while blocking the cave by an outside wall to imprison his father, the boy takes pity on him and so he leaves a small opening for his father to breathe in some fresh air. Moreover, he decides to return regularly to nourish him with goat’s milk.
It just happens that on the same day that the son takes over his father’s farming duties, the king issues an edict by which he dictates that as from now on all his subjects should leave their working place and toil only the king’s fields. When visiting his father that evening, the young lad confided in him the news.
The old man tells him, ‘If the king wishes that you take care of his fields then do so. Till his fields during the day, but also make sure that you work our own fields during the night. The boy agrees and he manages to till both the king’s land as well as that of his own family. Harvest time comes and he is the only one in the kingdom who successfully harvests both the king’s crops as well as his own. The king is puzzled as to how the boy manages to gain such a good harvest in both cases. So he summons the young lad to demand an explanation. The boy admits to the king about his working both fields each day, one in the morning and one at night. The king is amazed at the boy’s skills and astuteness.
‘Young man, you seem to be quite a shrewd fellow. So now you must do this for me’, says the king: ‘Tomorrow you must come to visit me on foot but also riding a donkey’.
The boy goes back to his father’s cavern to seek advice as how to solve this problem. The father tells him: ‘Oh that may be simpler than you think. Choose a donkey of a modest size. Mount her but ensure that while riding her your feet keep threading the ground. Then walk, while astride the donkey all the way up to the palace. That should satisfy the king’s wishes.’
The boy did this and when summoned by the king the following morning he rode his donkey all the way to the king’s palace while threading his feet on the ground. The king greets him and laughs, ‘My goodness you are a clever lad’. ‘And now that you have passed two tests, you have still another challenge to face, so hear this: tomorrow you must come to me barefooted but at the same time wearing a pair of boots’.
This mystifying challenge once again made the boy run back to his father’s cave for help. The father scratches his head for a moment, but soon comes up with a solution. He tells his son: ‘Take your boots to a cobbler and tell him to strip off the sole of each shoe. Then wear your shoes and go to the king as the heels of your feet are touching the ground. In this manner you will be both clad in your shoes and at the same time you remain barefooted!’ This is exactly what the boy does, and so he walks in the soleless boots all the way to the king’s palace.
The king asks the boy, ‘how is it that you seem to find a solution to all my challenges?’ and the boy says that it is his father from his sepulchral grave who gives him advice. ‘You mean to say that your dead father speaks to you?’ – ‘No’, says the boy, ‘my father is alive, but he is locked up in one of the sepulchral caves’. The king shakes his head in disapproval. He immediately issues an edict that forbade anyone to lock up their aged parents in caves when nearing the end of their lives. And since then, no more dying people in that kingdom were being locked up.
While these amusing tales were simply meant to delight children, the stories were also a way to impart moral lessons to any listener. Faced with peculiar and perilous situations the heroes of the tale found fortitude and solutions to their challenges by thinking outside the box, as the modern saying goes.
* The Maltese used to call the Grand Master of the Order of St John that ruled Malta (1530 – 1798) is-Sultan. Indeed, there is a placename known as Ġnien is-Sultan, near Rabat, and Bieb is-Sultan, a gateway into the Cottonera Fortifications.
* * *
Bibliography Cassar Pullicino Joseph, Studies in Maltese Folklore, Malta University Press, 1992. Magri Manwel, Ħrejjef Missirijietna, Provinċja Maltija ta’ Ġesu, 1967. Mifsud Chircop Ġorġ, Manwel Magri – Ħrejjef Missirijietna, Publishers Enterprises Group, 1994. Grima Lily, Stumme’s Folktales from Malta, Malta University Publishing, 2019.A * B * Ċ * C * D * E * F *
Ġ * G * GĦ * H * Ħ * I * J * K *
L * M * N * O * P * Q * R * S *
T * U * V * W * X * Ż * Z *
To read more on Maltese folk and culture, in particular to Maltese humour, please click here: https://sites.google.com/view/maltesehumoursbutseriously/home This book deals with the story of Maltese humour since Roman times up to present.
This book deals with the story of Maltese humour since Roman times up to present.
The author tackles humour both on the individual level as well as that which was and is presented in the theatre and on screen. The writer draws from many past and present anecdotal episodes and situations to elucidate on the genral state of the Maltese psyche. Humour is a two way style of communication that sizes up the temperament of both the presenter as well as the receiver of humour.
Paperback; paġni: 226. Euro 12.95. Available at bookstores …. If you are in Valletta try Agenda or Meli Bookshops.
Also available in ebook format from Amazon Kindle. Price: $.7.30.
Please click here to know more:Pubblikazzjonijiet

Excellent articles 🙂
LikeLike